What is DevOps? A Guide to Culture, Tools, and Practices
TL;DR
DevOps is a cultural philosophy that combines practices and tools to shorten the software development lifecycle and deliver high-quality applications faster. It focuses on breaking down silos and improving collaboration between Development (Dev) and Operations (Ops) teams. The CAMS model defines its four pillars: Culture, Automation, Measurement, and Sharing. Key practices include Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD), and Infrastructure as Code (IaC). The ultimate goal is to increase an organization's speed and reliability in delivering software, creating a more efficient and responsive workflow.
DevOps is a cultural and professional movement that combines philosophies, practices, and tools to deliver applications and services at scale. It addresses the historical friction between development teams, who want to ship new features quickly, and operations teams, who prioritize stability and reliability.
By breaking down these traditional silos, DevOps fosters a collaborative environment where teams share responsibility throughout the entire application lifecycle. This approach helps organizations build, test, and release software faster and more reliably.
A Practical Definition of DevOps
It's easy to get confused about what DevOps actually is. Is it a job title, a specific team, a set of tools, or a rigid methodology? The answer is that it’s a combination of all these things, but at its heart, DevOps is a cultural shift.
It represents a combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools designed to shorten the software development lifecycle. The core goal is to enable continuous delivery with high software quality by improving communication and collaboration between Dev and Ops teams.
Two popular frameworks help clarify the essential components of a successful DevOps implementation.
The Core Components of DevOps
Understanding DevOps is easier when you break it down into its foundational elements. The CAMS and Trinity models provide clear structures for thinking about how to implement it.
The CAMS Model
The CAMS model, often attributed to John Willis and Damon Edwards, outlines the four pillars of DevOps:
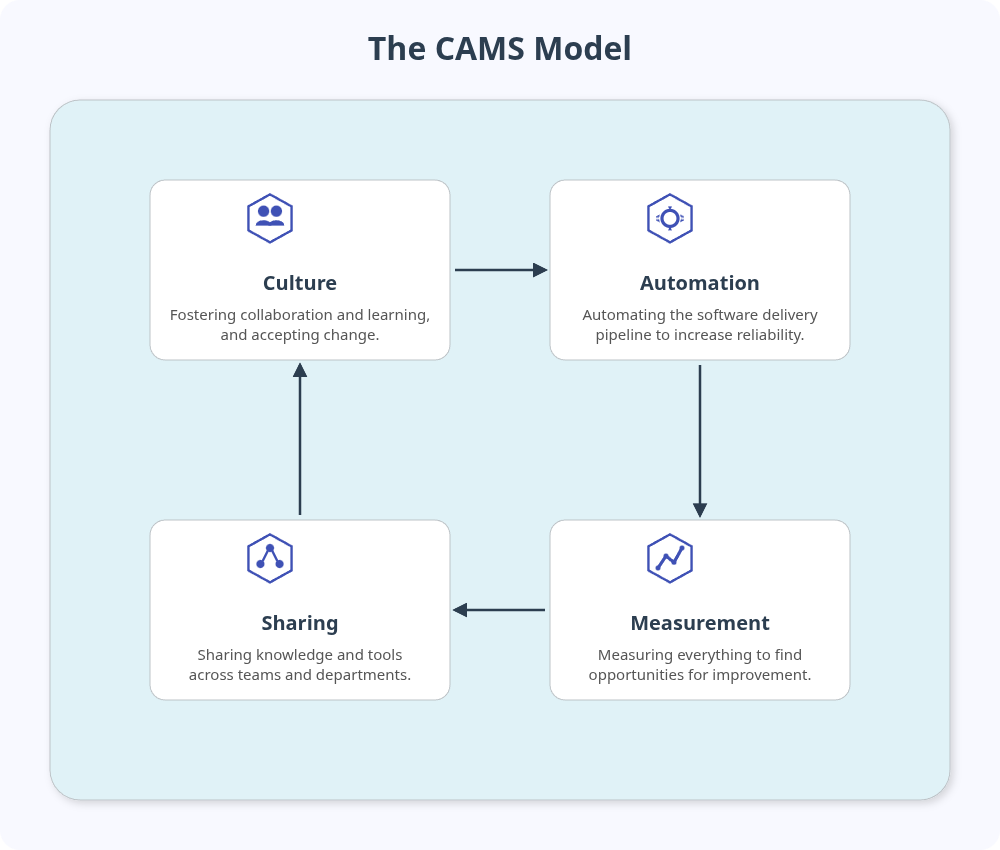
- Culture: This is the most important element. It is about fostering collaboration, shared responsibility and trust between teams. An important practice is to conduct no-blame post-mortems to focus on fixing systemic issues rather than assigning blame.
- Automation: Automating repetitive and manual tasks is essential for speed and consistency. This includes automating the build, test, deployment, and infrastructure provisioning stages of the software delivery pipeline.
- Measurement: You can't improve what you don't measure. DevOps relies on continuously monitoring performance, collecting feedback, and using data to identify bottlenecks and drive improvements across the lifecycle.
- Sharing: Encouraging the open sharing of knowledge, tools, successes, and failures across all teams is vital. This transparency helps build a collective sense of ownership and accelerates learning.
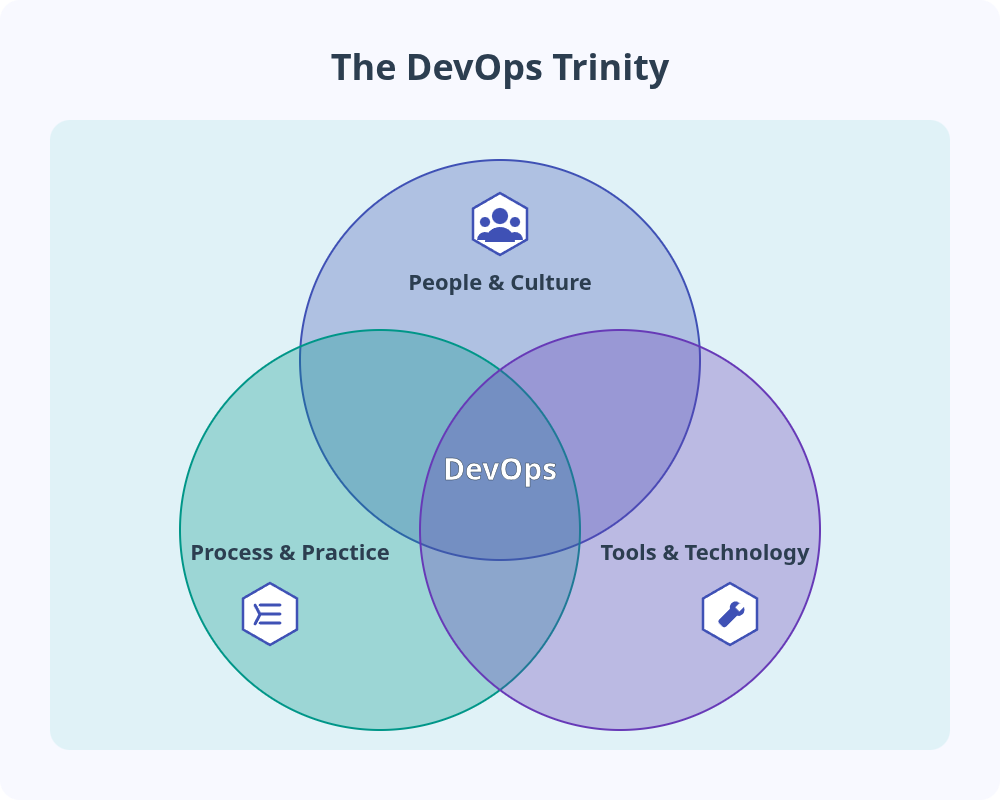
The DevOps Trinity
The DevOps Trinity, proposed by Brian Dawson, views the practice as three interconnected areas working in harmony:
- People & Culture: This focuses on how teams are structured and interact. It emphasizes shared values that prioritize collaboration, efficiency, and continuous improvement.
- Process & Practice: This includes the specific workflows and methodologies that teams adopt. Common practices are Agile development, Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD), and Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
- Tools & Technology: This refers to the software, platforms, and infrastructure that enable automation and support the chosen processes. Examples include version control systems (like Git), CI/CD servers (like Jenkins or GitLab CI), monitoring tools, and cloud platforms (like AWS, Azure, or GCP).
Ultimately, DevOps represents a fundamental shift in how development and operations teams collaborate, transitioning from isolated functions to a highly integrated and collaborative partnership. For a deeper look at performance metrics, the annual DORA State of DevOps Report is an excellent resource.
🗃️ Docker
3 items
🗃️ Kubernetes
2 items
🗃️ Infrastructure as Code
1 item